A B2B comparison evaluating high-grade GRS (Global Recycled Standard) cotton crochet lace against standard cotton sewing trim across production cost, stability, raw material supply, and factory line adaptability—designed to help ODMs and brands decide which trim best supports scalable sustainable product programs.
Definitions: What are High-Grade GRS Cotton Crochet Lace and Standard Cotton Sewing Trim?
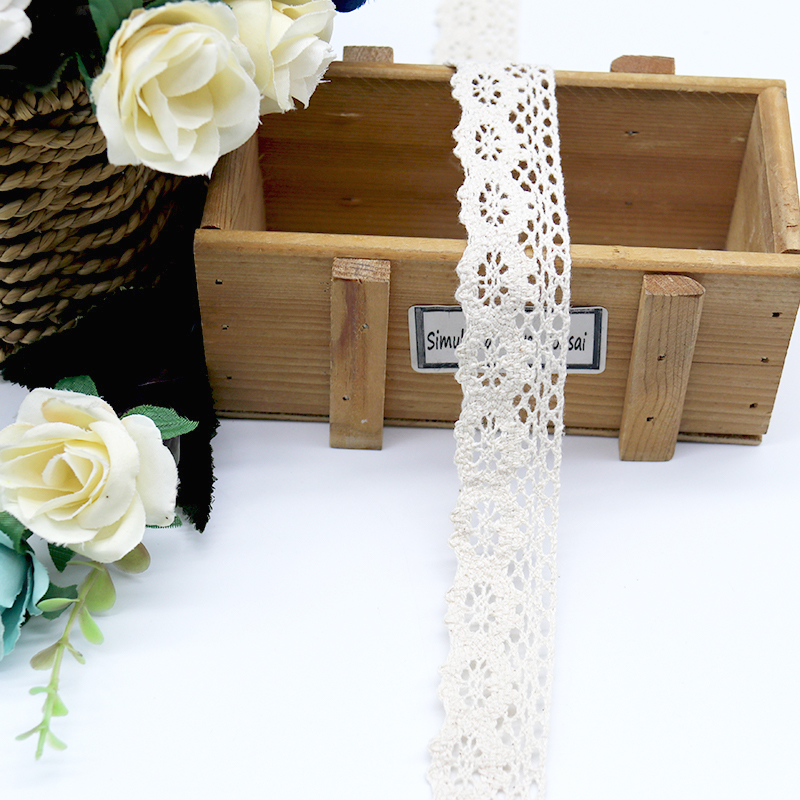
High-Grade GRS Cotton Crochet Lace
- Crochet lace produced from cotton yarns certified under the Global Recycled Standard (GRS), indicating recycled content, chain-of-custody, and environmental/social compliance.
- Typically positioned as a premium sustainable trim — hand-crochet or machine-crochet styles, openwork patterns, used for visible decorative elements.
Standard Cotton Sewing Trim
- Conventional cotton trims (braids, eyelets, narrow lace, cotton ribbon) made from virgin or conventionally produced cotton without recycled certification.
- Often produced on narrow-loom or embroidery equipment; cost-optimized for high-volume garment assemblies.
Definitions: What are High-Grade GRS Cotton Crochet Lace and Standard Cotton Sewing Trim?
What is GRS certification in textiles?
The Global Recycled Standard (GRS) is an international certification that verifies the recycled content of products and ensures responsible social, environmental, and chemical practices in their production.
What are common types of sewing trims used in garments?
Common sewing trims include lace, ribbons, piping, bias tape, and fringe, which are used to enhance the aesthetic appeal and functionality of garments.
Production cost comparison: raw materials, processing, certification, and per-unit economics
Raw material cost
Processing & labor
- Crochet lace (even machine-crochet) is more intricate — higher machine time or skilled labor input than many narrow trims; increases per-meter cost.
- Standard sewing trims benefit from faster, highly automated production on narrow fabric or embroidery lines; lower labor per unit.
Certification & compliance overhead
- GRS adds audit costs, documentation, potential segregation logistics (higher OPEX).
- Standard cotton has minimal certification overhead unless OEKO-TEX/organic claims are pursued.
Yield, waste & finishing
- Crochet lace may have higher trimming/finish labor; water or dye finishing for GRS yarns may need compliant processes.
- Standard trims often have optimized finishing, lower scrap.
Per-unit economics (practical view)
- For identical widths/complexity, expect GRS crochet lace > standard cotton trim in cost; gap narrows with scale and direct sourcing from certified mills.
How does GRS certification impact production costs?
Obtaining GRS certification can increase production costs due to the need for sourcing certified recycled materials, implementing sustainable practices, and undergoing regular audits to maintain certification standards.
What factors influence the cost of producing cotton crochet lace?
Factors include the complexity of the design, production method (handmade vs. machine-made), labor costs, and the quality of the cotton used.
Stability & quality consistency: performance, testing, and production tolerances
Dimensional stability & performance
- Crochet lace (natural cotton) can relax or deform under tension/wash unless preshrunk or blended; GRS yarns should meet same textile performance specs if properly processed.
- Standard cotton trim produced on stable narrow-loom platforms typically shows higher repeatability and edge stability.
Colorfastness & finishing
- Recycled cotton may react differently to dyes; tighter quality control required to ensure colorfastness and batch match.
- Standard cotton processes are well-established for consistent dye lot matching.
Batch-to-batch consistency
- Machine-processed crochet lace with controlled yarn specs can be consistent, but artisanal variants yield variability.
- Standard trims from automated lines deliver predictable tolerances, ideal for OEM repeatability.
Testing needs for B2B procurement
- Tensile, wash/humidity, colorfastness, and dimensional change tests should be mandatory for GRS trims; acceptance criteria must be in SOW.
What tests are conducted to ensure the quality of sewing trims?
Common tests include assessments for colorfastness, tensile strength, shrinkage, and durability to ensure trims maintain their appearance and function over time.
How do production tolerances affect the quality of lace trims?
Strict production tolerances ensure consistency in size, pattern, and quality, reducing defects and ensuring uniformity across batches.
Raw material supply and sourcing risks: availability, traceability, and price volatility
Supply availability
Traceability & documentation
- GRS requires chain-of-custody, certificates, and audits — beneficial for brand transparency but adds procurement complexity.
Price volatility & contract strategy
- Recycled cotton prices can be higher and more volatile due to feedstock availability; forward contracts and long-term supplier partnerships reduce risk.
Risk mitigation approaches
- Dual-sourcing (certified mills + backup), buffer inventory, and collaborative forecasting with suppliers help stabilize supply for GRS trims.
What are the challenges in sourcing recycled cotton for GRS-certified products?
Challenges include ensuring a consistent supply of high-quality recycled cotton, maintaining traceability throughout the supply chain, and managing potential price fluctuations due to limited availability.
How does cotton price volatility impact the production of sewing trims?
Fluctuations in cotton prices can affect production costs, leading to variability in the pricing of sewing trims and potentially impacting profit margins.
Factory adaptability: machinery, workflows, QA, and traceability on the production floor
Equipment & process fit
- Crochet lace production: either specialized crochet machines or skilled handwork; may require slower cycles and more operator skill.
- Standard cotton sewing trim: produced on high-speed narrow looms, ribbon machines, or standard embroidery lines—optimized for volume.
Line integration & throughput
- Standard trims integrate directly into high-speed garment assembly lines with minimal disruption.
- Crochet lace (especially wider or delicate pieces) may require separate finishing, careful handling, and slower feed rates—affecting takt time.
Quality control & segregation
- GRS products need segregation and traceability from yarn receipt through to final packing to maintain certification claims—software and floor labeling procedures required.
- Standard trims have simpler QA workflows; less paperwork.
Investment & operational impact
- Producing GRS crochet lace at scale can mean retrofitting lines, training operators, and adding documentation steps—capex/OPEX that must be justified by volume and margin.
What machinery is required for producing high-quality crochet lace?
Producing high-quality crochet lace typically requires specialized crochet machines capable of handling intricate patterns and ensuring consistent stitch quality.
How can factories ensure traceability in the production of sewing trims?
Factories can implement comprehensive tracking systems, maintain detailed records of materials and processes, and conduct regular audits to ensure traceability and compliance with standards.
Application scenarios & strategic recommendations for sustainable ODM initiatives
Best-fit applications for High-Grade GRS Cotton Crochet Lace
- Premium sustainable collections (eco-lingerie, organic cotton apparel, bridal lines with sustainability story), limited-edition capsules, premium children’s wear where natural and recycled messaging adds value.
- Where trim is a visible brand differentiator and consumers pay a margin for sustainability.
Best-fit applications for Standard Cotton Sewing Trim
Go-to-market & positioning strategies for ODMs
- Tiered SKU strategy: offer standard trims for core price-sensitive SKUs; reserve GRS crochet lace for premium sustainable SKUs.
- Pilot program: run small-batch GRS lace collections to validate supply, costs, and consumer uptake before committing to scale.
- Certification-based marketing: leverage GRS certificates in marketing collateral and tech packs for retail partners.
Commercial and operational tactics to scale GRS trims
- Negotiate long-term supply agreements with certified yarn mills to secure pricing and capacity.
- Invest in supplier development and shared forecasting to reduce lead times.
- Standardize design templates for crochet lace to enable partial automation and reduce per-unit labor.
- Implement traceability systems (lot tracking, QR codes) to preserve GRS claims across the supply chain.
How can ODMs integrate sustainable practices in trim production?
Original Design Manufacturers (ODMs) can integrate sustainable practices by sourcing eco-friendly materials, obtaining certifications like GRS, optimizing production processes to reduce waste, and implementing recycling programs.
What are the benefits of using GRS-certified trims in garment manufacturing?
Using GRS-certified trims enhances brand reputation, appeals to environmentally conscious consumers, ensures compliance with sustainability regulations, and contributes to environmental conservation efforts.
Conclusion and recommended next steps for B2B adoption
Summary judgment
- For large-scale, cost-driven OEM production where throughput, stability, and low unit cost are primary, standard cotton sewing trim remains the pragmatic choice.
- For ODM initiatives specifically targeting sustainability, brand differentiation, and higher-margin segments, high-grade GRS cotton crochet lace aligns better—provided supply, certification, and production workflows are managed proactively.
Recommended phased approach for ODMs and brands
- Define target SKUs and pricing tiers: map which SKUs justify GRS premium.
- Run a pilot (small MOQ) with certified suppliers to test quality, wash performance, and consumer feedback.
- Secure supplier agreements with GRS mills (minimum commitments, lead-time SLAs).
- Upgrade factory procedures: add segregation, traceability, and targeted QC checkpoints.
- Scale gradually and monitor unit economics—adjust sourcing mix and margins.
Final note for procurement teams
- Treat GRS crochet lace as a strategic investment in brand value and sustainability compliance rather than a drop-in replacement for commodity trims; plan sourcing, production, and marketing in an integrated way to capture both commercial and ESG benefits.

John Gan
John Gan specializes in professional lace and fabric customization, leading Shaoxing Yituo to expand globally with quality and innovation. He is committed to making the company a leading supplier through strong international partnerships.